Table of Contents
Staying organized with your project management responsibilities may seem overwhelming, but with the proper database and system, it’s more manageable than you might imagine. This blog post explores the significance of maintaining an efficient project management database and provides guidance on getting started.
What is a project management database?
A project management database is a centralized repository of information that facilitates the organization, storage, and retrieval of data related to project management activities. It serves as a structured system for managing and tracking various aspects of a project, such as tasks, timelines, resources, budgets, and team collaboration.
Key features of a project management database may include:
- Task Management: Tracking and organizing tasks, assignments, and milestones within a project.

- Resource Allocation: Managing and assigning resources efficiently to ensure optimal utilization.
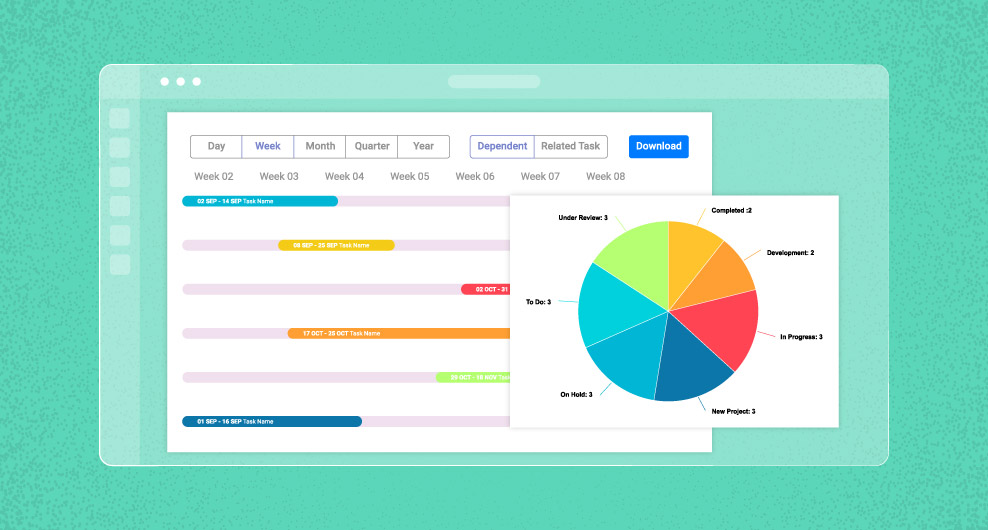
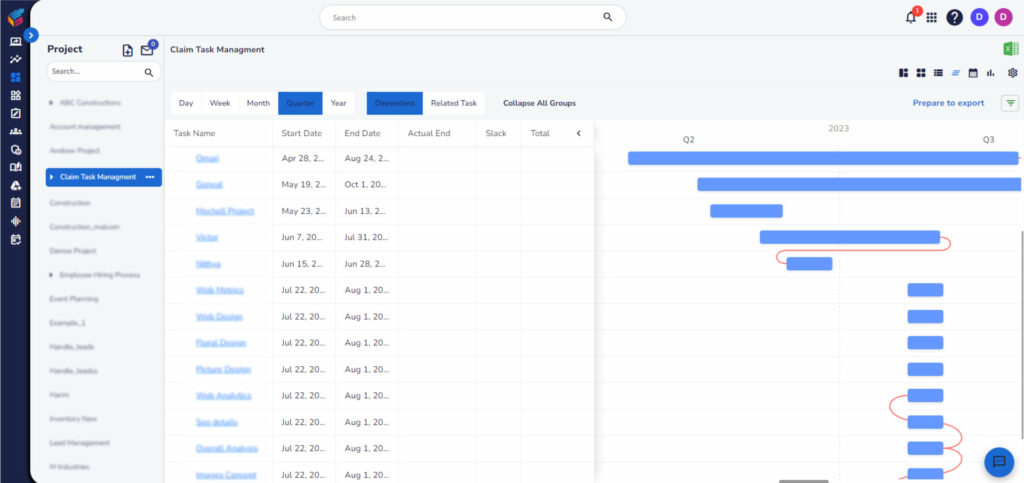
- Timeline and Schedule: Creating and maintaining project timelines, project schedules, and deadlines.
- Budget Tracking: Monitoring project expenditures and budget allocation to prevent overruns.
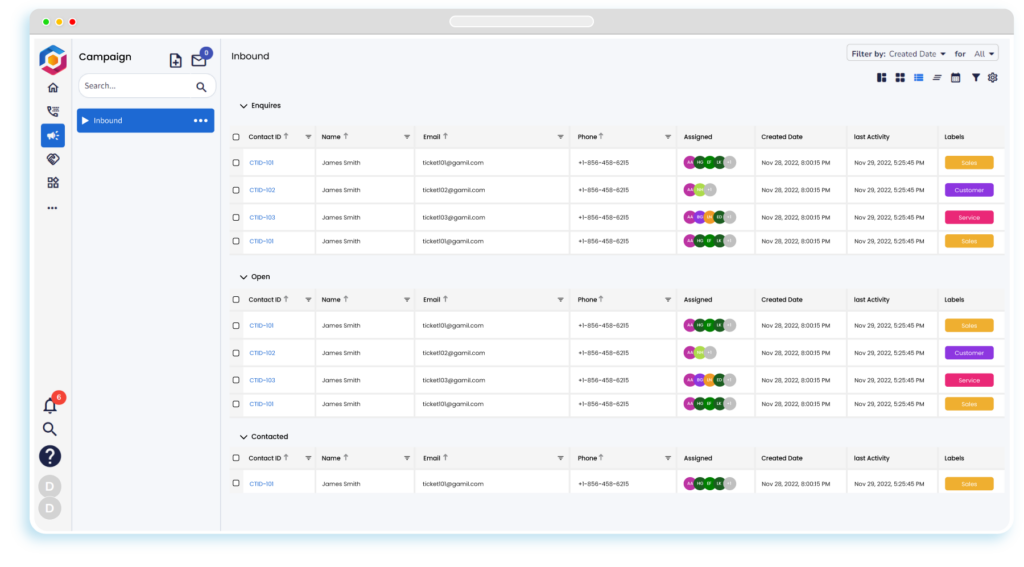
- Collaboration: Providing a platform for team members to communicate, share documents, and collaborate on project-related activities.
- Risk Management: Identifying and managing potential risks that may impact on the project’s success.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generating reports and analytics to evaluate project progress, performance, and areas for improvement.
By utilizing a project management database, teams can enhance communication, streamline workflows, and maintain a comprehensive overview of project-related information. This, in turn, contributes to effective decision-making and successful project completion.
Why is it important to maintain a project management database?
Maintaining a project management database is crucial for several reasons:
- Centralized Information: A project management database serves as a centralized repository for all project-related information. This ensures that all team members have access to the latest and most accurate data, promoting consistency and reducing the likelihood of errors or miscommunication.
- Improved Organization: The database allows for the systematic organization of project elements such as tasks, timelines, resources, and budgets. This organization enhances overall project structure, making it easier to manage and navigate through complex project landscapes.
- Enhanced Collaboration: A well-maintained project management database facilitates collaboration among team members. It provides a platform for sharing updates, documents, and feedback, fostering a collaborative environment that contributes to better decision-making and problem-solving.
- Efficient Resource Management: The database enables efficient allocation and tracking of resources. This ensures that team members are assigned tasks according to their skills and availability, preventing overloading or underutilization of resources.
- Real-time Monitoring: By maintaining a project management database, project managers can monitor progress in real time. This allows for quick identification of potential issues, timely interventions, and adjustments to keep the project on track.
- Risk Mitigation: The database supports effective risk management by providing a platform to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. This proactive approach helps in anticipating challenges and developing strategies to address them, reducing the impact of unforeseen issues.
- Historical Data and Analysis: Over time, the database accumulates historical data about project performance. This information can be valuable for post-project analysis, lessons learned, and continuous improvement. It provides insights into what worked well and areas that may need improvement in future projects.
- Client and Stakeholder Communication: A project management database facilitates transparent communication with clients and stakeholders. It allows for sharing progress reports, timelines, and key milestones, fostering trust and ensuring that everyone involved is well-informed.
Maintaining a project management database promotes efficiency, collaboration, and transparency, leading to successful project outcomes and improved overall project management processes.
Benefits of maintaining a project management database
Here are additional benefits of maintaining a project management database:
- Facilitates Scalability: As projects grow in complexity or team size, a well-maintained database can easily scale to accommodate increased data and user requirements. This adaptability is essential for handling larger and more intricate projects.
- Document Version Control: The database helps in maintaining version control for project documents. This ensures that team members are working with the latest versions of documents, preventing errors and confusion that may arise from using outdated information.
- Improved Decision-making: Access to accurate and real-time data allows project managers to make informed decisions quickly. This is particularly valuable when faced with unexpected challenges or changes in project requirements, enabling a more agile and responsive project management approach.
- Enhances Client Satisfaction: Through transparent communication and timely reporting, a project management database contributes to improved client satisfaction. Clients can easily track project progress, leading to a stronger client-provider relationship and increased satisfaction with project outcomes.
- Compliance and Audit Trail: For projects in regulated industries, maintaining a project management database helps in ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. The database also provides an audit trail, allowing for a thorough review of project activities if needed.
- Streamlines Onboarding of New Team Members: A centralized database aids in the onboarding process for new team members. They can quickly familiarize themselves with project details, timelines, and assigned tasks, reducing the learning curve and enabling them to contribute more effectively from the start.
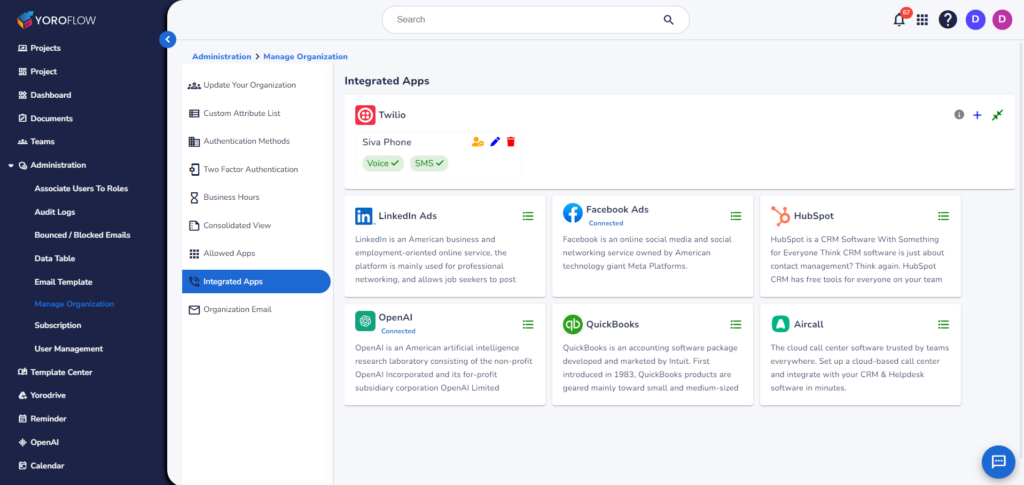
- Integration with Other Tools: Many project management databases can integrate with other tools and software, such as communication platforms, productivity tools, and analytics software. This integration streamlines workflows and enhances overall project efficiency.
- Encourages Standardization: By providing a standardized framework for project management, a database promotes consistency in processes and documentation. This standardization simplifies project management across various teams and projects, leading to a more efficient and cohesive work environment.
- Remote Collaboration: In an era of remote work, a project management database becomes even more essential for facilitating collaboration among team members who may be geographically dispersed. It provides a virtual workspace where team members can coordinate and communicate effectively.
- Measurable Performance Metrics: The database allows for the tracking and measurement of key performance indicators (KPIs). This data-driven approach enables project managers to assess project performance objectively and identify areas for improvement in future projects.
A well-maintained project management database offers a wide range of benefits, from facilitating collaboration to supporting scalability and improving decision-making. Its impact extends across various aspects of project management, contributing to the overall success of projects.
Conclusion
In summary, the upkeep of a project management database is imperative for organizations aiming to adeptly oversee their projects. This system offers an effective means of storing and retrieving project data, fostering enhanced collaboration among teams.
Furthermore, it enables organizations to monitor project advancement, pinpoint challenges, and uphold project timelines. A robust project management database not only ensures the timely achievement of goals but also furnishes essential data for precise reporting, contributing to the overall success of the organization’s project management endeavors.