Table of Contents
Vendor management encompasses the diverse business processes undertaken by organizations collaborating with multiple suppliers and vendors to control costs, mitigate risks, and provide excellent service. It enables companies to optimize costs, minimize potential risks, and ensure high-quality service delivery— all while effectively managing relationships with numerous vendors and suppliers.
This guide comprehensively covers various vendor management types, breaks down the entire process into actionable steps, addresses the anticipated challenges, and introduces the best vendor management system (VMS) to adeptly manage your supplier relationships.
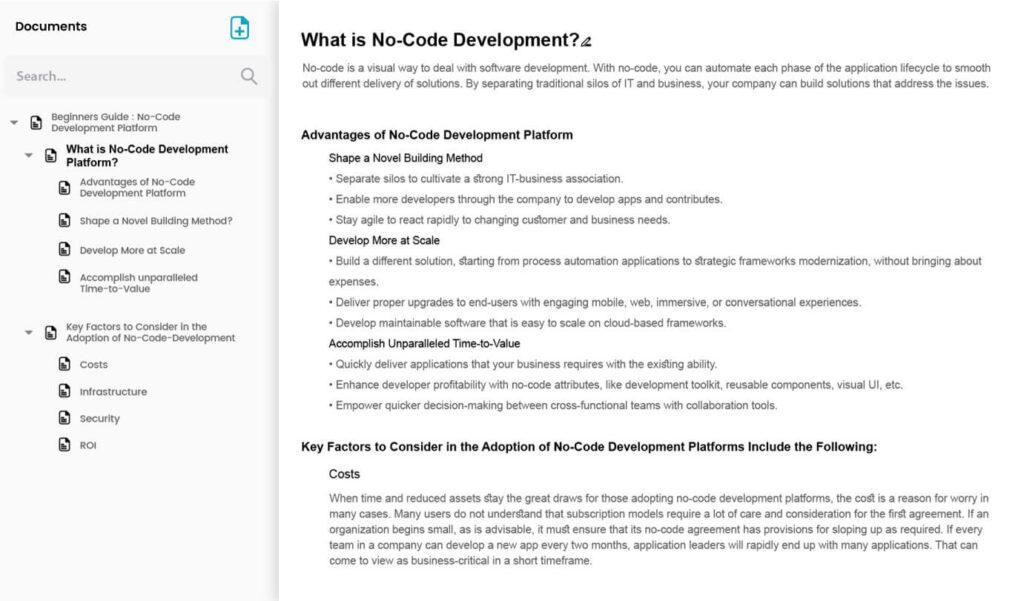
What is the Definition of Vendor Management
Vendor Management refers to the disciplined process of strategically overseeing and optimizing supplier relationships to ensure seamless collaboration and achieve business objectives. It involves a structured approach to managing suppliers, enhancing business processes, and contributing to the success of the procure-to-pay process.
What is the Process of Vendor Management
The following steps outline a comprehensive Vendor Management process to ensure seamless collaboration and successful procurement operations.
Identification of Vendor Requirements:
- Begin by identifying the specific goods or services your organization requires.
- Clearly outline the criteria and expectations for potential vendors.
Vendor Selection and Evaluation:
- Conduct a thorough evaluation of potential vendors based on criteria such as reputation, reliability, pricing, and past performance.
- Create a shortlist of vendors that align with your organization’s needs.
Request for Proposal (RFP) or Quotation (RFQ):
- Issue an RFP or RFQ to the selected vendors, detailing the requirements and expectations.
- Gather and evaluate the proposals, considering factors such as cost, delivery timelines, and quality.
Contract Negotiation and Agreement:
- Engage in negotiations with the selected vendor to finalize terms, conditions, and pricing.
- Develop a comprehensive contract that clearly outlines expectations, deliverables, and performance metrics.
Onboarding and Vendor Registration:
- Once a vendor is selected and a contract is in place, initiate the onboarding process.
- Register the vendor in your system, ensuring all necessary documentation is collected and compliance requirements are met.
Performance Monitoring and Metrics:
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure vendor performance.
- Regularly monitor and assess vendor performance against agreed-upon metrics.
Communication and Relationship Building:
- Foster open communication channels with vendors to address concerns and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Build strong relationships to enhance collaboration and understanding between the organization and its vendors.
Risk Management and Compliance:
- Implement a robust risk management strategy, identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with vendor relationships.
- Ensure vendors comply with relevant regulations, industry standards, and contractual agreements.
Invoice Management and Payment:
- Implement efficient systems for managing vendor invoices, ensuring accuracy and timely processing.
- Adhere to agreed-upon payment terms and promptly settle invoices to maintain positive vendor relationships.
Continuous Improvement:
- Regularly review and assess the effectiveness of Vendor Management processes.
- Seek feedback from internal stakeholders and vendors to identify areas for improvement.
Performance Reviews and Renewal:
- Conduct periodic performance reviews with vendors to assess ongoing collaboration.
- Determine whether to renew, renegotiate, or terminate contracts based on performance evaluations.
Documentation and Record Keeping:
- Maintain thorough documentation of all vendor-related activities, contracts, and communications.
- Ensure compliance with record-keeping requirements for audit and reference purposes.
By diligently following these steps in the Vendor Management process, organizations can establish and maintain effective supplier relationships, optimize procurement operations, and contribute to the overall success of the business.
Effective Tools for Vendor Management: Streamlining Supplier Relationships
Leveraging technology is crucial for streamlining these processes. Here are few effective tools for Vendor Management that can significantly contribute to the success of procurement operations:
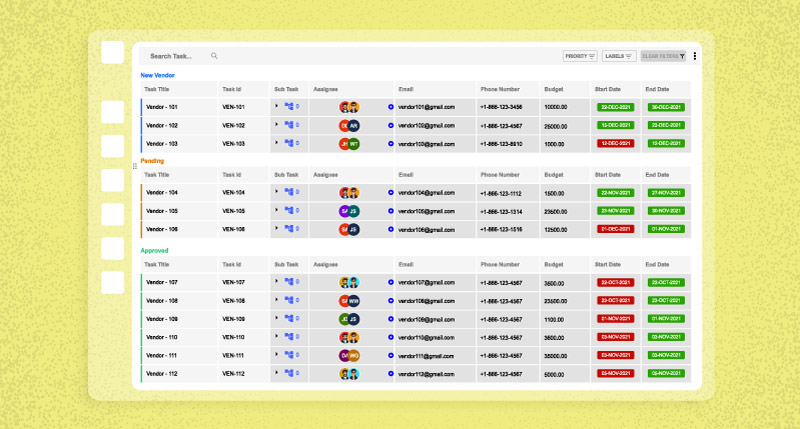
Vendor Management Systems (VMS):
- Automated Supplier Onboarding: Simplifies and accelerates the vendor onboarding process.
- Performance Evaluation: Provides tools for assessing and tracking vendor performance.
- Contract Management: Streamlines the management of vendor contracts and agreements.
- Communication Tools: Facilitates seamless communication between organizations and vendors.
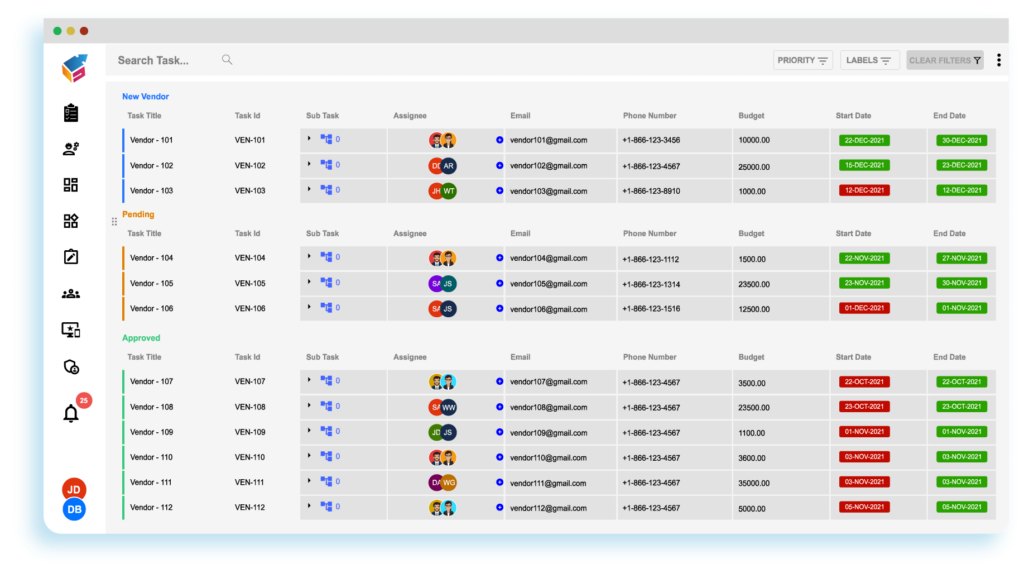
Procurement Software:
- Purchase Order Management: Automates the creation and tracking of purchase orders.
- Invoice Management: Streamlines the processing and approval of vendor invoices.
- Vendor Collaboration: Enhances collaboration between organizations and vendors in real-time.
- Spend Analysis: Provides insights into procurement spending patterns for informed decision-making.
Project Management Tools:
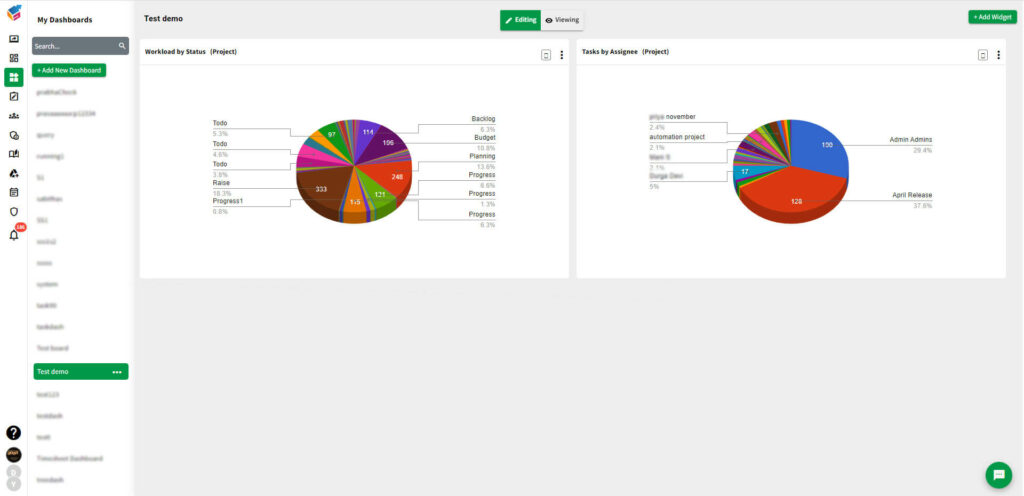
- Approval Workflow: Facilitates a structured approval process for project-related activities.
- Task Management: Organizes and tracks tasks associated with vendor projects.
- Collaboration Platforms: Enables effective communication and collaboration among project stakeholders.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides project performance insights for strategic decision-making.
- Incorporating Project management tools like Yoroproject, which includes a structured project management approval workflow, enhances project management processes, promoting efficiency, collaboration, and contributing to the overall success of your projects.
Process Automation Solutions:
- Workflow Automation: Automates routine Vendor Management tasks, reducing manual effort.
- Data Integration: Integrates seamlessly with other organizational systems for data consistency.
- Alerts and Notifications: Sends timely alerts for critical events and deadlines.
- Compliance Monitoring: Automates compliance checks to ensure adherence to policies and regulations.
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) Tools:
- Relationship Tracking: Monitors and tracks the status of relationships with various suppliers.
- Collaboration Portals: Provides a centralized platform for effective collaboration.
- Risk Management: Assesses and mitigates risks associated with specific suppliers.
- Performance Analytics: Offers analytics for evaluating supplier performance over time.
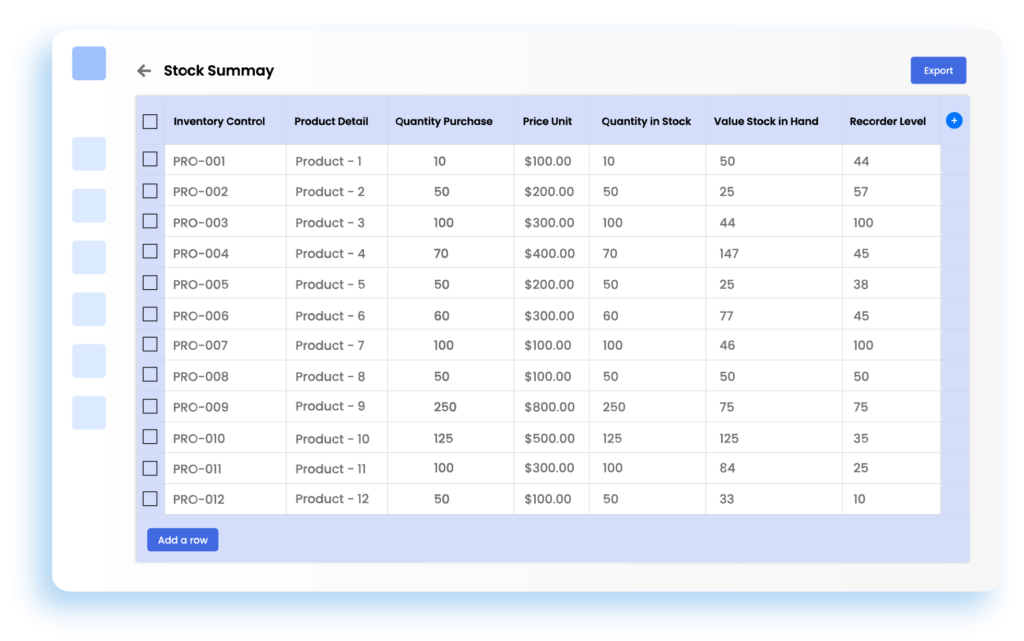
Document Management Systems:
- Centralized Document Repository: Stores and organizes all vendor-related documents in one location.
- Version Control: Manages different versions of contracts, agreements, and other documents.
- Access Control: Ensures secure access to sensitive vendor information.
- Audit Trails: Maintains a record of document changes and user actions.
Communication and Collaboration Platforms:
- Real-time Messaging: Facilitates instant communication between the organization and vendors.
- Document Sharing: Allows for the secure sharing of files and information.
- Video Conferencing: Enhances virtual collaboration for more effective communication.
- Activity Feeds: Provides a timeline of interactions and updates related to vendor relationships.
Data Analytics Tools:
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizes data to predict future trends and potential challenges.
- Performance Dashboards: Offers a visual representation of key performance indicators.
- Spend Analysis: Analysis of spending into procurement to identify cost-saving opportunities.
- Vendor Scorecards: Creates scorecards for evaluating and comparing vendor performance.
Incorporating these effective tools into Vendor Management processes empowers organizations to streamline operations, enhance communication, and foster strong and mutually beneficial relationships with suppliers. Choosing the right combination of tools depends on the specific needs and objectives of the organization, ensuring a customized and efficient Vendor Management strategy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective Vendor Management is indispensable for businesses seeking to optimize their procurement processes and foster strong supplier relationships. By embracing technology, automating key processes, and utilizing purpose-built tools, organizations can navigate the complexities of Vendor Management with precision, ensuring a seamless and cost-effective procure-to-pay process.