Table of Contents
Say you’re closing deals at an excellent rate—you should meet your quota for the month. But what about next month? In sales, consistency is key. When you don’t have a framework for successful sales, you won’t be able to predict your sales for tomorrow, let alone next month or next quarter.
Without a strategy, you’re navigating with no map and no idea where to go next. If you’re doing well, you won’t know how to repeat that success, and if you’re doing poorly, you won’t know how to avoid failure next time around. The solution? Create a sales cycle.
What is a sales cycle?
A sales cycle is the step-by-step process that a salesperson or a business follows to close a sale successfully. It encompasses all the stages from initially identifying a potential customer or lead to ultimately converting them into a paying customer. The specific steps in a sales cycle can vary depending on the industry, product, or service, but common stages include prospecting, qualifying leads, making a sales pitch, handling objections, closing the deal, and post-sale follow-up.
The purpose of a sales cycle is to provide a systematic and organized approach to selling, helping sales professionals to understand where a potential customer is in the buying process and what actions need to be taken to move them closer to making a purchase. By having a well-defined sales cycle, businesses can improve efficiency, track progress, and enhance the overall effectiveness of their sales efforts.
Why is the sales cycle important?
The sales cycle is important for several reasons, playing a critical role in the success of a business or salesperson. Here are some key reasons why the sales cycle is important:
- Organization and Structure: A sales cycle provides a structured framework for the sales process, helping sales teams stay organized and follow a systematic approach to selling. This structure ensures that no critical steps are overlooked and that each stage is addressed appropriately.
- Efficiency: By having a predefined sales cycle, sales professionals can work more efficiently. They can focus on the most promising leads, prioritize tasks, and allocate resources effectively. This efficiency contributes to time management and productivity.
- Understanding Customer Needs: The sales cycle involves various stages of interaction with potential customers. This allows salespeople to better understand the needs, preferences, and challenges of their customers. This understanding is crucial for tailoring sales efforts to meet customer expectations.
- Forecasting and Planning: A well-defined sales cycle enables businesses to forecast sales more accurately. By tracking progress through each stage, sales teams can anticipate future sales, set realistic targets, and plan resources accordingly.
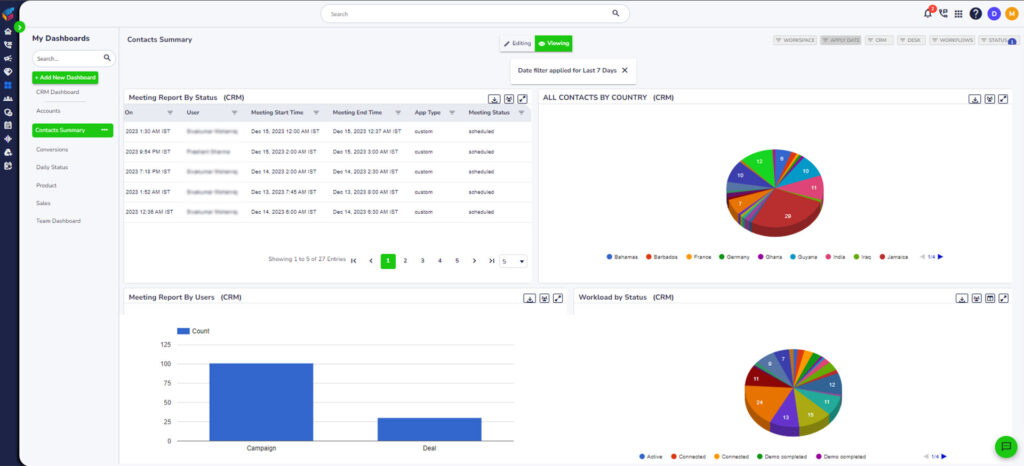
- Consistency and Replicability: A standardized sales cycle promotes consistency in sales efforts. Successful strategies can be identified and replicated, and unsuccessful ones can be modified or eliminated. This consistency helps build a reliable and predictable sales process.
- Customer Relationship Management: The sales cycle includes post-sale activities, such as follow-ups and customer support. This ongoing relationship management is crucial for customer satisfaction, loyalty, and potential repeat business. A positive customer experience can lead to referrals and positive word-of-mouth.
- Adaptability and Improvement: Monitoring the sales cycle allows businesses to identify areas for improvement. By analyzing each stage, sales teams can adapt their strategies, refine their approaches, and continuously improve their overall sales performance.
- Decision-Making: A well-documented sales cycle provides valuable data for decision-making. Business leaders can assess the effectiveness of different strategies, allocate resources wisely, and make informed decisions about sales tactics and investments.
Improving customers’ perception of your brand requires a strategic and proactive approach. Here are four steps to help enhance how customers perceive your brand:
What are the 7 stages of a sales cycle?
The stages of a sales cycle can vary slightly depending on the source and the nature of the sales process.
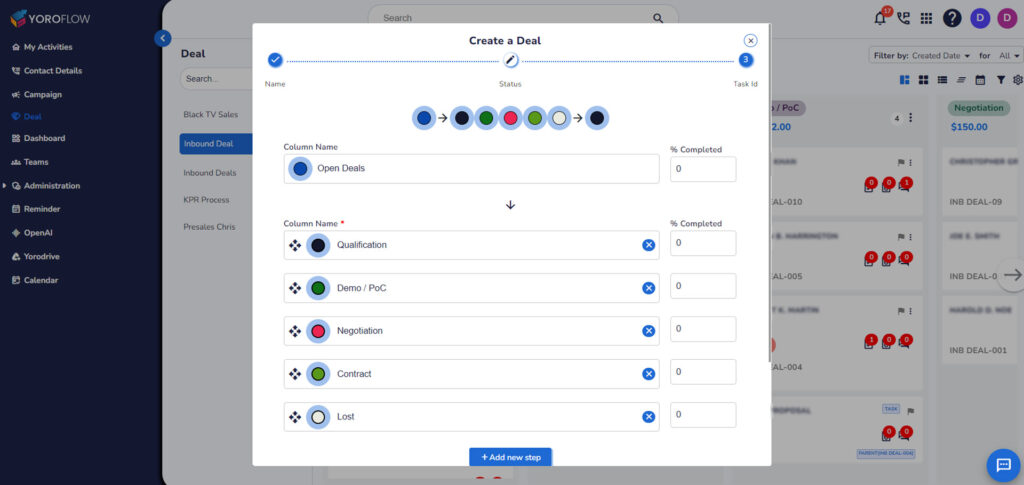
However, a commonly recognized model includes the following seven stages:
Prospecting:
In this initial stage, the focus is on identifying potential customers or leads. This involves researching and reaching out to individuals or businesses that may have an interest in the product or service.
Qualification:
Once leads are identified, the next step is to qualify them. This involves assessing whether the leads have the potential to become actual customers. Qualification criteria may include factors like budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT).
Needs Analysis:
In this stage, the salesperson works to understand the specific needs, challenges, and goals of the potential customer. This involves gathering information through conversations, surveys, or other means to tailor the sales approach.
Presentation:
Armed with an understanding of the customer’s needs, the salesperson presents a tailored solution. This stage involves showcasing the product or service, highlighting its features and benefits, and addressing how it meets the customer’s requirements.
Handling Objections:
It’s common for customers to raise concerns or objections during the sales process. This stage involves addressing these objections and providing additional information or clarification to alleviate any hesitations the customer may have.
Closing the Deal:
The closing stage is where the salesperson asks for the sale. This can involve finalizing details, discussing terms, and guiding the customer toward making a purchase decision. Effective closing techniques are crucial at this stage.
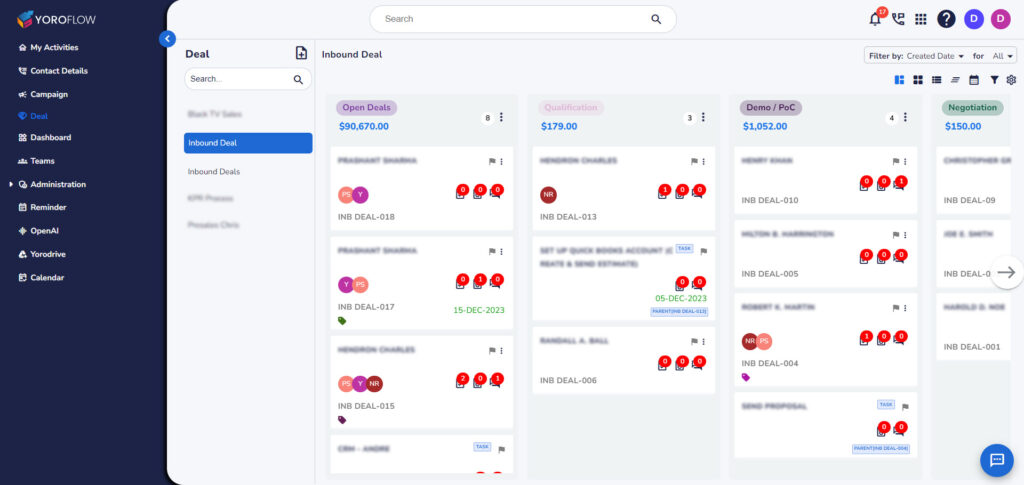
Follow-Up and Maintenance:
After the sale is closed, the relationship doesn’t end. This stage involves post-sale activities, such as follow-up calls, providing support, and ensuring customer satisfaction. Building a positive post-sale relationship can lead to repeat business and referrals.
While these stages provide a general framework, it’s important to note that sales cycles can be iterative, and the stages may overlap or repeat as needed. Additionally, different industries and businesses may have variations in their sales cycle stages based on their unique processes and customer interactions.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve shared strategies to enhance your sales cycle, let’s explore additional keys to effectively managing this process. Firstly, stay vigilant for bottlenecks and pain points where both your sales team and customers commonly encounter challenges. It could be that your team faces difficulties in lead generation, necessitating closer collaboration with marketing to ensure a robust pipeline. Alternatively, your team may possess a substantial lead list, but consistently encounters issues with converting those leads into prospects.
Quality control is another vital consideration. Devote time to review phone and video recordings, as well as email threads, to uncover any communication issues with potential customers. It’s possible that your sales team may struggle with presenting to prospects or closing deals.
Here’s where a user-friendly CRM system proves invaluable. For instance, using YoroCRM provides comprehensive insights into every facet of your sales team’s efforts, empowering you to devise targeted training plans for overall success.
Ready to elevate your sales cycle and propel your team’s performance to new heights? Take advantage of a free trial by signing up today.




