Table of Contents
Sales teams often face challenges while maintaining consistency within their sales processes, leading to missed opportunities and occasionally neglecting essential parts of the sales cycle. Here‘s when the sales process flowchart comes to the rescue.
A sales process flowchart is a potent tool, enabling sales teams to establish a well-structured framework for their sales cycle. It simplifies the tracking of all sales operations for sales managers, decision-makers, and other stakeholders.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the sales process flowchart and the essential steps required to create one successfully.
Are you curious to get started? Let’s begin by defining the sales process flowchart.
What is a Sales Process Flowchart?
A Sales Process Flowchart is a graphical representation or diagram that visually depicts the structured sequence of steps and stages within a sales process, extending from the initial lead generation to the critical stage of deal closure. This visual tool offers a well-organized, at-a-glance overview of the entire sales journey, encompassing essential tasks, decision points, and potential outcomes at each juncture.
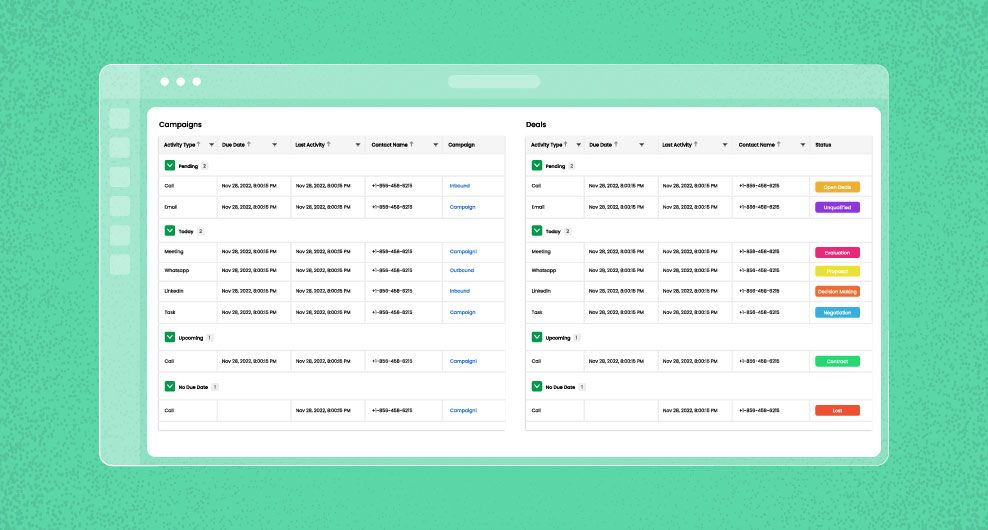
Sales teams utilize these flowcharts to standardize and streamline their sales procedures, thereby simplifying the comprehension, management, and enhancement of the sales cycle. The sales process is successful through tools and technologies like CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems, sales automation software, and sales playbooks to help manage leads, track customer interactions, and ensure a consistent and effective sales approach.
While the specific stages and steps may vary depending on the company, industry, and product or service, a typical sales process often includes the following key components:
- Prospecting: Find out and produce leads, or prospective clients, who are interested in the good or service.
- Qualification: Evaluating leads to ascertain their suitability as potential clients by considering facts like their requirements, budget, and decision-making authority in making purchases.
- Needs Analysis: Gaining insight into the prospect’s needs and areas of concern to personalize the sales pitch effectively.
- Presentation and Demonstration: Showcasing the product or service’s features and benefits to the prospect.
- Handling Objections: Addressing concerns, questions, or objections that the prospect may have.
- Closing: Encouraging the prospect to make a purchase, reach a decision, or sign a contract.
- Follow-up: Maintain post-sales communication and ensure customer satisfaction.
- Post-sale Activities: Manage account relationships, provide support, and seek opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
The sales process is a strategic framework that helps sales teams improve efficiency, close rates, and customer relationships. Tailoring the sales process to an organization’s specific requirements and objectives can enhance its efficacy.
Guidelines for Crafting an Efficient Sales Process Flowchart
An effective sales process flowchart is essential for a well-organized and efficient sales operation. Here are some practical tips to make the process user-friendly:
- Start with a Clear Objective: You can start by defining an essential goal of your sales process flowchart. Understanding the purpose will guide you in creating a chart that serves its intended function effectively.
- Simplify the Steps: Keep the flowchart simple and concise. Avoid clutter and overly complex symbols. The goal is to make it easy for everyone to understand and follow.
- Involve Your Team: Engage your sales team in the creation process. Their insights and experiences can help you capture the actual workflow accurately.
- Use Standard Symbols: Employ universally recognized flowchart symbols for processes, decisions, and connectors. Consistency in your chart makes it easier to interpret.
- Define Stages Clearly: Clearly label each stage of the sales process and provide a brief description of the activities or tasks that occur at each stage.
- Highlight Decision Points: Identify key decision points and use diamond-shaped symbols in the operation. Clearly state the criteria or choices that affect the flow.
- Show Dependencies: Use arrows to demonstrate the sequence of activities and any dependencies between stages. It helps maintain a logical order.
- Account for Variations: Acknowledge that not all leads follow the same path. Design your flowchart to accommodate different scenarios or customer types.
- Incorporate Key Metrics: Include relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) at each stage to measure the effectiveness of your sales process.
- Maintain Clarity: Avoid jargon and keep descriptions simple and understandable to the audience. The flowchart should be easily accessible and understandable for everyone involved.
- Regular Updates: The sales process is dynamic. Ensure your flowchart evolves with changes in the market, customer behavior, or your products/services.
- Training Tool: Use the flowchart as a training resource for new team members. It provides a visual guide to help them understand and navigate the sales process.
- Integration with Tools: Ensure your CRM system and sales automation tools align with the flowchart. This integration can streamline operations further.
Creating an effective sales process flowchart simplifies complex workflows, aligns your team’s efforts, and enhances overall sales efficiency. Keep it user-friendly, regularly updated, and in sync with your sales tools to achieve optimal results.
Real-Life Examples
Let’s delve into real-life scenarios to see how practical concepts work.
- Retail Sales Process: In a retail environment, the sales process flowchart takes shape from the moment a customer enters the store (lead generation) to the point of sale (deal closure). A sales automation platform might help manage inventory and optimize product placement in the sales pipeline, while the sales team uses a sales playbook to ensure consistent customer interactions.
- B2B Sales Process: B2B sales involve intricate lead management. Here, the CRM system is pivotal in storing essential client information. Process mapping is critical, as businesses need to define the steps from lead generation to deal closure. It includes lead nurturing through tailored presentations and negotiations with potential clients.
Applications of a Sales Process Flowchart
Now, let’s explore the practical applications of a well-structured sales process flowchart.
- Sales Pipeline Optimization: By mapping out the sales process, companies can identify bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement within their sales pipeline. It ensures that leads progress smoothly from the top of the sales funnel to deal closure.
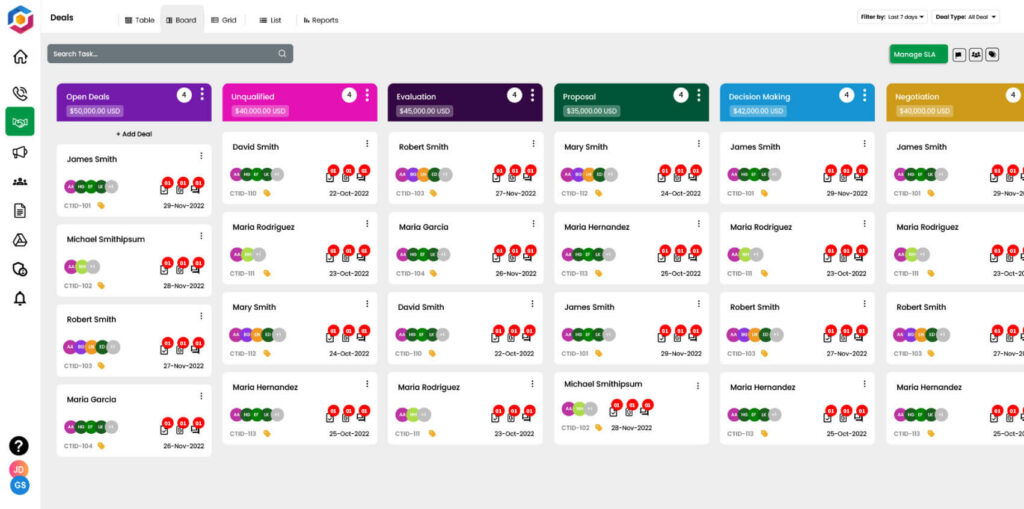
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Organizations can successfully collect and analyze data by integrating a CRM system with a sales process flowchart. This data-driven approach helps in making informed decisions and aligning sales strategies with lead-generation efforts.
- Enhanced Lead Nurturing: Organizations may create lead nurturing strategies that work by a defined process that guarantees prospective clients get the correct information at the right moment.
A well-crafted sales playbook provides guidelines for personalized customer interactions.
Conclusion
The sales process flowchart is a powerful tool for businesses, providing a clear path from lead generation to deal closure. Real-life examples demonstrate its versatility in different industries, from retail to B2B sales. Its applications, including sales automation and CRM integration, help organizations streamline operations and enhance decision-making. Embracing this approach is essential to long-term success in sales and marketing.