Table of Contents
In the dynamic landscape of project management, leads and lags are the guiding stars that ensure a seamless journey toward success. These strategic tools, akin to the conductor’s baton in an orchestra, allow project managers to harmonize diverse tasks, resources, and timelines.
Join us as we delve into the intricacies of leads and lags, unlocking their transformative power to drive projects to new heights. Through real-world examples and practical applications, you will discover how mastering these dependencies can be the key to achieving your project’s full potential.
Get ready to embark on a journey that will revolutionize your approach to project management and set your projects on a trajectory of unparalleled success.
What is Project Management?
Project management is a structured approach to planning, organizing, executing, and controlling projects. A project, in this context, is a temporary endeavor with a specific goal, a defined scope, a set timeline, and allocated resources. The primary purpose of project management is to ensure that the completion of the project meets its objectives while staying within budget and adhering to the specified schedule.
Project management software is a valuable tool that aids project managers in organizing tasks, collaborating with team members, and keeping all project-related information in one place. It enhances efficiency, transparency, and communication, making it an integral part of modern project management practices across various industries and domains.
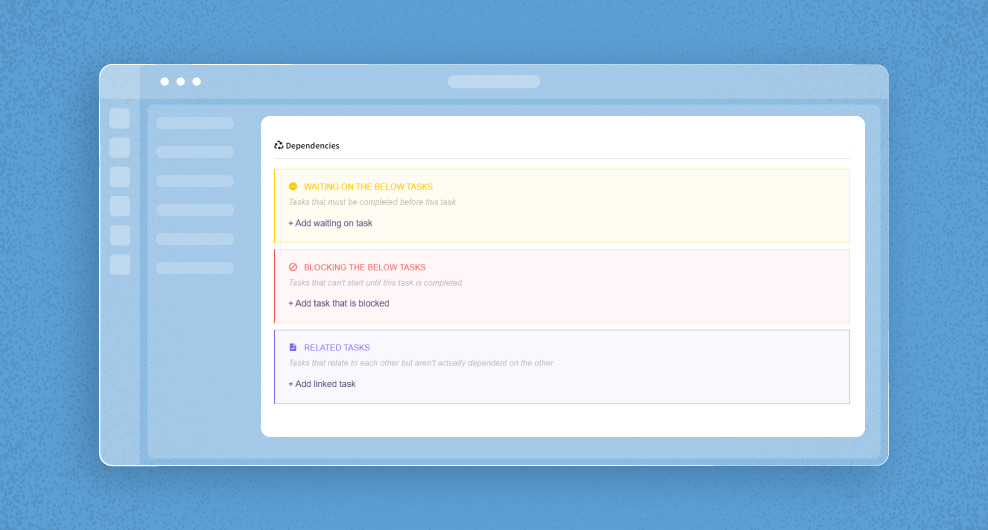
What Are the Leads and Lags in Project Management?
In project management, “leads” and “lags” are terms used to describe the relationships between tasks in a project schedule.
A “lead” is a scheduling term that refers to accelerating a successor task, enabling it to start before its predecessor task is complete. It implies the successor task can show the way to project deadlines and commence earlier than planned, reducing the overall project duration. Lead often maximizes concurrent task execution chances to improve productivity and fulfill project deadlines.
Conversely, a “lag” is a delay or waiting period introduced between the completion of one task and the start of its successor task. Insert lags for specific reasons, such as when there is a need to create a time gap between tasks. For instance, in a construction project, a lag might introduced between pouring concrete and removing the formwork to allow the concrete to set correctly.
In lead and lag management, project managers strategically employ these concepts to optimize task sequencing, resource allocation, and project timeline.
Purposes of Leads and Lags in Project Management
Leads and lags are used in project management to manage and optimize the sequencing of tasks within a project schedule. They serve several purposes:
Leads:
- Acceleration: Leads allow a successor task to start before its predecessor task is complete. It can accelerate the project schedule and help in meeting project deadlines.
- Concurrent Task Execution: They make it possible for activities to overlap, encouraging parallel labor and cutting down on the total project duration.
- Resource Efficiency: Leads can help ensure that critical resources are allocated effectively and are not idle, improving resource utilization.
- Risk Mitigation: By allowing particular tasks to start early, leads can build buffers into the project schedule, protecting against unexpected delays.
Lags:
- Task Dependencies: By employing lags, natural task relationships and constraints are considered. They ensure that one task does not start too early or too late about another task.
- Resource Availability: Lags can accommodate situations where a resource needed for the succeeding task is not immediately available, ensuring the task scheduling in a resource-efficient manner.
- Regulatory Compliance: They can introduce to comply with external constraints or regulatory requirements and ensure the tasks’ performance in the proper sequence.
- Safety and Quality: Lags might inserted to allocate time for quality control, safety measures, or other processes between tasks, improving the quality and safety of the project.
- Lead Time: In some cases, lags provide lead time for the succeeding task to prepare, gather necessary resources, or make adequate preparations.
Both leads and lags are essential tools for project managers to create realistic and efficient project schedules that meet project objectives effectively.
Optimizing Leads and Lags in Project Management
Managing leads and lags in projects efficiently is crucial for optimizing your project schedule and ensuring task dependencies align with your project timeline. Know some tips for lead management.
- Understanding Task Dependencies: Before utilizing leads and lags, comprehensively map out task dependencies in your project schedule. It forms the foundation for identifying where leads and lags can be most beneficial.
- Applying Leads Strategically: Find opportunities to use leads to expedite important routes or permit work to overlap. Carefully assess which tasks can benefit from lead time to accelerate the project schedule.
- Leveraging Gantt Charts: Gantt charts are invaluable for visualizing task dependencies and lead time within your project timeline. Use Gantt charts to identify potential areas for lead management.
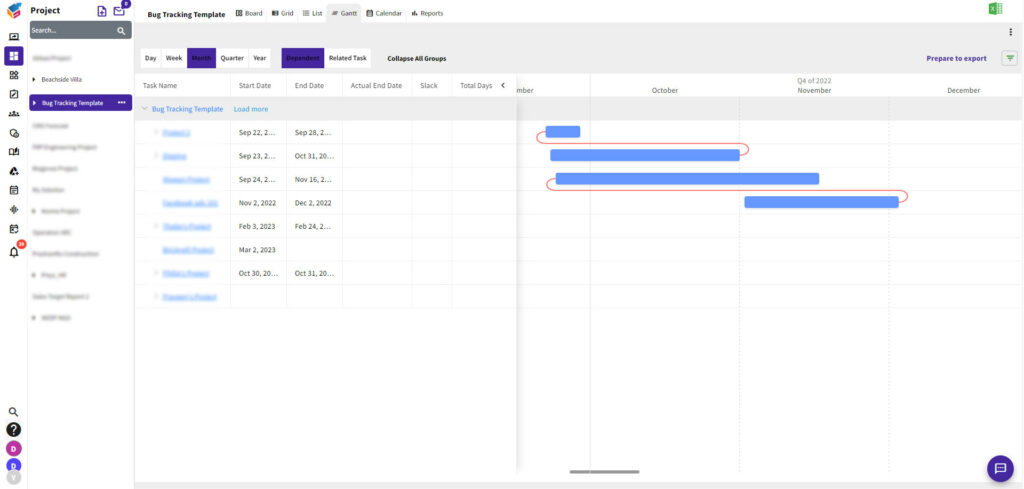
- Introducing Lags Purposefully: When inserting lag time, do so with specific purposes in mind. Ensure that lags align with the natural progression of tasks, resource availability, safety measures, or regulatory requirements.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: Continuously monitor your project’s progress and the impact of leads and lags. Be prepared to adjust necessary to keep the project on track and meet milestones.
- Kanban Board for Work Management: Use a Kanban board to visualize and manage work tasks in real-time. It can help in coordinating tasks and ensuring that work proceeds smoothly.
- Collaboration and Communication: Effective communication among team members is essential for lead management. Discuss the leads and lags used with your team to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding task sequencing.
- Resource Allocation: When applying leads, consider how this may affect resource allocation. Ensure that resources are effectively utilized and not overburdened.
By implementing these tips, you can enhance lead management in your projects, better utilize project management tools like Kanban boards and Gantt charts, and maintain a well-structured project schedule that aligns with task dependencies and meets your project timeline effectively.
Final Thoughts
In the world of project management, harnessing the power of strategic dependency management is the key to unlocking your project’s true potential. By skillfully navigating leads and lags, you can orchestrate tasks, resources, and timelines with precision, ensuring your projects soar to new heights of success. It is time to seize the reins of project management, master the art of dependency management, and watch your projects thrive as they have never done before.