Have you ever heard of the phrase “the best-laid plans often go awry”? That statement is so true in the world of project management.
What is a Project Management Methodology?
Project management methodologies ensure that the project is finished on time and within budget. A project management methodology will usually cover different areas such as managing deliverables, resource allocation, change control, and more.
Approaches to Selecting a Project Management Methodology
A project management methodology is a set of principles, processes, and tools used to manage the work involved in a project.
Below are the top 6 project management methodologies:
Top 6 Popular Project Management Methodologies and When to Use Them
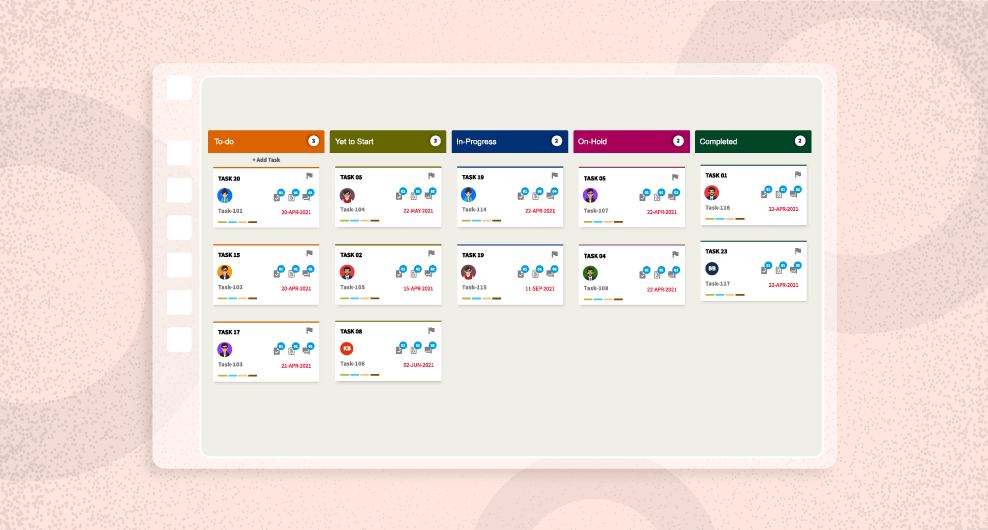
Kanban
Scrum
Jeff Sutherland and Ken Schwaber developed the Scrum project management methodology, which is a short-term approach aimed at accelerating project timelines for timely, within-budget delivery, and high-quality product management. There are four main steps to using Scrum for your project: planning, executing, monitoring, and adjusting.
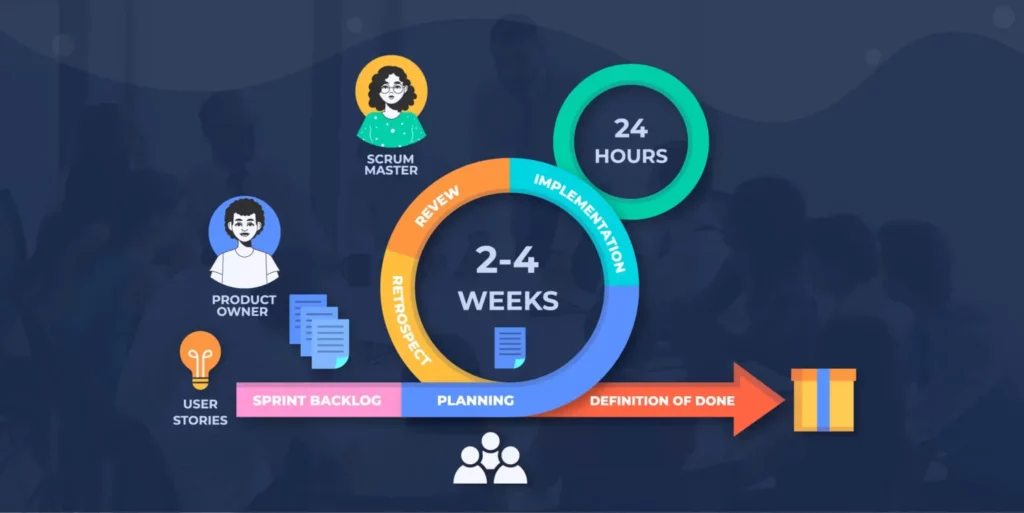
The Scrum Project Management methodology is one of the most well-known. It divides the project planner into two phases: product discovery and development. In the product discovery phase, teams need to discover what they can do with a fixed budget and time frame. Once this has been done, they start developing their project.
Lean
Lean Project Management (LPM) is a set of guidelines and practices that focus on the customer-focused delivery of products, encompassing project tracking, task management, project phases, project timeline, project management scope, and project life cycle. It provides a framework for all project managers to deliver a product or service that is on time, within budget, and meets the customer’s needs. LPM originates from lean production practices designed to reduce waste, extending beyond manufacturing.

In development for the past 30 years, lean project management aims to reduce waste and maximize time through total customer focus. Traditionally, firms have relied on linear methods with high costs and low value-add. The key distinction of Lean projects is their encouragement of starting with an initial assumption, simplifying the process.
Agile
Agile project management is a popular software development methodology where an organization uses collaboration, flexibility, and change to create products or services quickly. Agile project management has been widely successful in software development, but it can also implement effectively in other industries. Implementing an agile methodology allows teams to adapt quickly to changing project requirements, fostering collaboration and delivering more effective and efficient results.
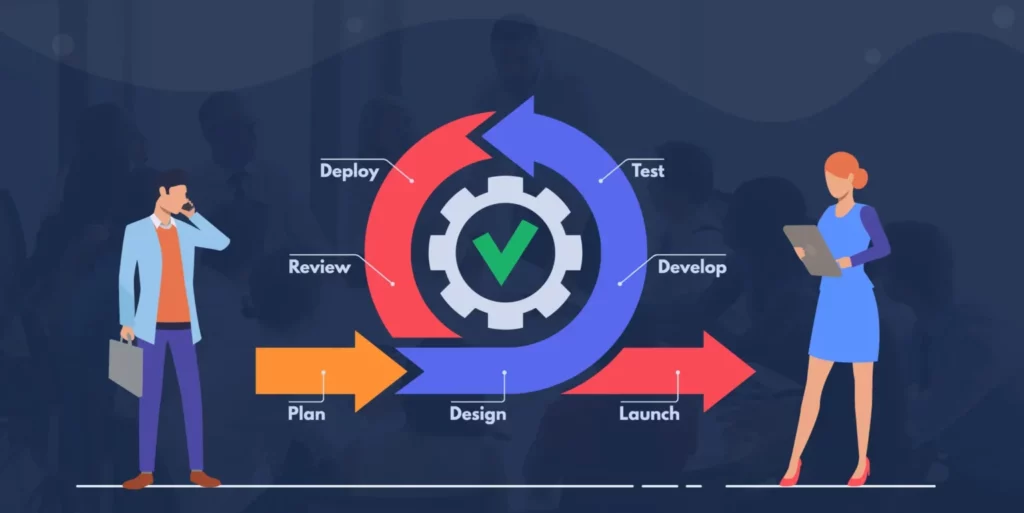
Agile project management was designed for short projects with a fixed time frame and known release date. It’s flexible enough to work on many different types of projects, and it provides a quick response from the development team. Supporters argue that this is even more important than long-term goals because it allows the team to take a shorter, more motivated approach to reach the goal.
Waterfall
Waterfall project management is a type of project management methodology that follows a step-by-step approach to planning, organizing, implementing, and monitoring the progress of a project. It’s commonly used in projects involving multiple organizations.
The Waterfall Project Management methodology is used to organize each stage of the project and the required resources for successful completion. This method has a linear approach, with all steps being completed in order before the project moves on to the next stage.
Hybrid
Hybrid Project Management is a combination of different project management methodologies. It merges the best of both worlds, making it a flexible and cost-effective project management methodology.
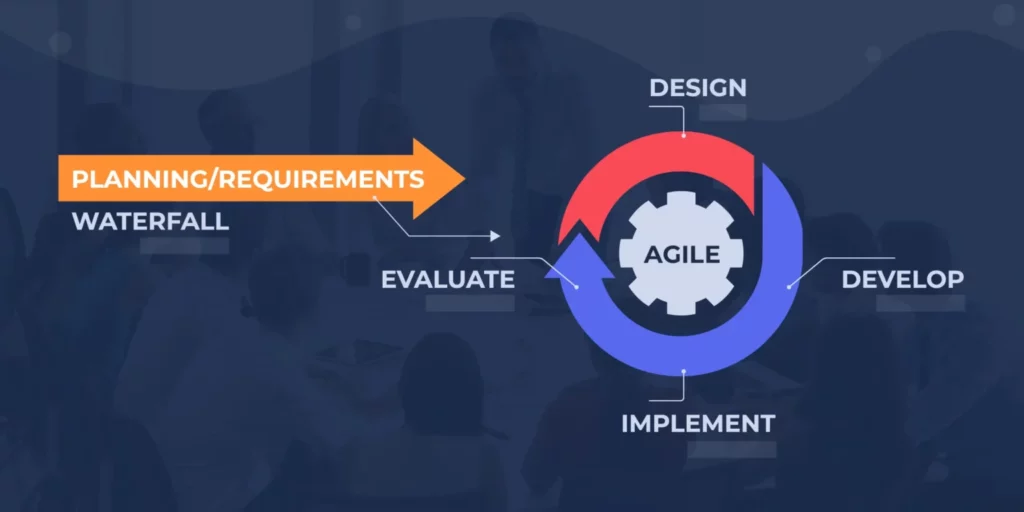
Hybrid Project Management (HP) is a project management methodology that combines traditional project management approaches elements. This approach focuses on maximizing solution opportunities and providing options for continuous improvement. It consists of an analytical, methodological, and situational analysis that uses an integrated model with multiple stakeholders, including cost-benefit research, business case development, and one-off decision making.